Royal Bank of Canada
Date: June 20th, 2020
Quick go through (Click):
Stability (includes industry analysis, COVID-19 impacts)
Valuation on the firm (DCF model etc.)
Value criteria 1: Low debt (Low bankruptcy risk)
Debt to equity ratio = 0.12 (calculation based on 2019 annual financial statement) < 1
* A high percentage of liability in a financial firm is the current liability, which is the saving people put in. because of that, debt to equity ratio is calculated differently. Long term debt is used to calculate debit to equity ratio.
Value criteria 2: Lack of liquidity
Current ratio = 1.17 (calculation based on 2019 annual financial statement)
The current ratio calculated from the annual data is slightly over 1. However, the current ratio calculated based on quarterly data shows that the current ratio of RBC remains at 0.9 during the past 5 years.
Source: Macrotrends
Value criteria 3: Long-term prospects
The greatest barrier to entry in banking is regulation. This comes from the fact that regulators ensure that there are only a few major banks in the country, and it is extremely difficult to regulate many banks. Additionally, controlling the number of large banks to a small number helps control the flow of money through the economy. There are two factors in the banking system that provide extra secure; low cost service, the safety and stability of the financial system. In order to enter the market, the company is required a significant amount of capital and governance.
In terms of withdrawing and depositing funds, there is no substitute product to banks except for credit unions. A survey conducted by FirstOntario Credit Union shows that approximately 40% of clients are dissatisfied with the services of their bank, and the service fees charged by banks and the fact that most credit unions do not charge service fees is a major part of this dissatisfaction.
Furthermore, banks also face threat from other non-financial competitors. The insurance companies and mutual fund companies provide banking services that can be also obtained from banks, while companies with big names are also offering new payment methods such as loans to attract more customers.
RBC continues to focus on extending their number one position in Canada as a leading financial institution by continuing to grow their volumes to increase market share. Internationally, they are “building premier, globally competitive businesses that primarily serve corporate, institutional and high net worth clients” (RBC).
RBC’s brand also helps to attract top-tier employees, which helps position their global franchise in capital markets and wealth management in order to deliver profitable long-term growth. With a combination of employee excellence and top-quality service they look attract new business from competitors with a core value-driven culture.
RBC aims to combat this issue by offering more end-to-end services, or “ecosystems” which covers wider customer needs than only financial, such as when they want to start their own business, sell their house, or find a new car.
Value criteria 4: Stability
Industry Analysis
In Canada there are a total of 88 banks and 5,907 branches across the country since 2017 (Canadian Bankers Association). The banking system in Canada is often referred to as being the safest in the world. However, the banking industry is highly cyclical to the economy activities.
According to PWC, there will be a major upskilling of the workforce in banking industry in 2020. By increasing use of electronic banking from customers and the growth of available data, banks in Canada have begun to focus on building a workforce with skills for a digital world.
Crypto currencies
Although the rise in use of crypto currency has drawn a great deal of focus from Canadian banks, the Bank of Canada is developing ways to better manage and safely invest with.
Impact of COVID-19 - volatility earnings
As of May 1, 2020, 11:00 am, the number of infected cases in Canada is 53,657. The virus spread largely in Canada and more significantly in the United States, many activities involve a large group of people would need to be cancelled or postponed.
With the sudden production suspension, it would lead to a shortage of demand and supply and a short-term loss of salary which increases the default rate. The Canadian and American administration have taken actions such as decrease the bank interest rate to prevent future erosion of the economy. RBC’s net income is unfavorably impacted by lower interest rate in Canada and the United States since it mainly operates in the two countries. Because of the potential effect on the net income of RBC, we can predict a lagged effect on the share price.
Personal banking contributes the highest percentage in banks’ revenue. In order to find out potential default risk, we can have a look on the S&P indices. The composite default index is a sum of the four types default indices, which includes auto default index, first mortgage default index, second mortgage default index, and bankcard default index.
Auto default rate and first mortgage default rate slightly decrease in the past 3 months. The bankcard default rate shows a relatively high increase of 0.99% over the past quarter. As of May 4th 2020, there is a relatively stable trend in the composite default index under the pandemic.
Bankcard default rate might not ramp up in the next quarter as people spend less due to the uncertainty of employment state. According to various public estimate, the credit card and debit card usage have declined about a range of 30% to 60%. On the other hand, the first mortgage default rate would see an increase if the government is failed to provide more financial support.
This is a good example that government’s financial support helps. On March 23rd, US federal government announced to provide another stimulus package, which is the unlimited assets purchase. Firms with financial issues can issue bonds during this time, and the government will promise to buy it. The steam of cash can help banks and other businesses to stay float and to solve the insolvency problem. On the same day, the stock market rebooted. The stock prices include RBC and other banks rallied.
Another thing to note is that the S&P auto default rate and bankcard default rate are fluctuated during the past three to five years. The banks have incorporated this factor in the risk model. RBC is able to comfortably handle the 5 year high in composite default rate, while also be preparing for a possible higher default rate due to the impact of the pandemic without having insolvency problem.
COVID-19 virus outbreak is a kind of systematic risk that many companies cannot eliminate. However, RBC’s risk control methods would help them mitigate and limit the potential effects from systematic risk. According to their 2019 annual report, they have two significant measures which are diversification and enterprise-wide stress testing program where helped them became one of the first companies recovered from 2008 recession.
According to an article in The Globe and Mail, RBC capital market’s staff has increased by 24% since 2008 and many bankers from Lehman Brothers, the fourth-largest investment bank in the United States in 2008, went to RBC to seek for job opportunities. After the corona virus outbreak, there would be many human resources available in the market result from the layoff due to the outbreak, and this provides a great opportunity for RBC to recruit more talents. On the other hand, we believe with the previous successful recover of RBC, it would convince investor to invest in RBC and its share price would rebound.






Source: National central banks, national government websites, ING, UBS, RBC GAM (as of March 23rd, 2020)
Source: S&P Indices and Experianas of April 2020
Source: S&P Indices and Experianas of April 2020
Source: S&P Indices and Experianas of April 2020


Source: Macrotrends
It shows in the graph above that RBC has a stable ROE at around 15% quarterly, while a 17.1% of annual ROE is shown in the 2019 annual report. If I ignore the impact of the pandemic on the firm’s profit, I believe this is a great indicator about the profitability of the firm.
The graph below presents the change in business revenue in quarter one 2020 sorted by sectors. Among the 20 different sectors, the lowest negative change is in finance and insurance sector, while this sector is below the average negative percent change of all industries. As the largest market capitalization bank in Canada, RBC’s revenue has a high weight in the sector. This shows that although interest rate decreases, the impact of the pandemic on the financial intuition’s earnings relatively remains low.
Consistent dividend payout record
An over ten-year unbroken dividend record can be observed in the graph below. During the 2008-2009 financial crisis, the firm was still able to pay out the dividends without decreasing the amount. RBC business model is to build customers a better future by consistently providing shareholders the greatest value. This dividend record shows that the firm is always striking for a profit share for investors.


Credit by me
Consistent growth in BV (past 4 years):
Royal Bank of Canada total assets for the quarter ending January 31, 2020 were $1,121.991B, a 9.38% increase year-over-year.
Royal Bank of Canada total assets for 2019 were $1075.131B, a 3.65% increase from 2018.
Royal Bank of Canada total assets for 2018 were $1037.222B, a 11.79% increase from 2017.
Royal Bank of Canada total assets for 2017 were $927.833B, a 4.22% increase from 2016.
Value criteria 5: Proper managerial incentives
RBC is a global financial institution with a purpose-driven, principles-led approach to delivering leading performance, and creating value for both their clients and communities. The governance team at RBC attempts to oversee RBC and its practices, while being transparent, independent of management, and ethical. RBC’s governance team understands that to be effective, the board must be independent of management. The board has a Director Independence Policy in place that incorporates regulations from the Bank Act and the Canadian Securities Administrators guidelines. To determine director’s independence, the board uses information about directors’ personal and business relationships with RBC, including their banking and financial information.
RBC has a policy that dictates directors who are also officers of RBC cannot receive any remuneration as directors. The maximum annual compensation that may be paid to executives is $6,000,000. As part of the board compensation program, directors must invest at least 40% of their annual board retainer in common shares or director deferred stock units which must be retained until retirement from the board. Since November 1, 2019, directors are required to own common shares or director deferred stock units with a minimum value of $1,200,000, or four times the board retainer within five years of joining the board, and directors are required to own a minimum of 1,000 common shares.
Currently RBC is not involved in any lawsuits by shareholders, however in 2014 Royal Bank of Canada had to pay $75.8 million in damages to former shareholders of Rural/Metro because it failed to disclose conflicts of interest in a $438 million buyout.
Value criteria 6: Comprehension
The services RBC provides include personal and commercial banking, wealth management, insurance, investor services, and capital markets products and services on a global basis. RBC’s performance over the last decade proved they are capable of not only broadening their expertise in all areas of consumer and corporate financial services but also made progress geographically. RBC continues to focus on extending their number one position in Canada as a leading financial institution by continuing to grow their volumes to increase market share. Internationally, they are “building premier, globally competitive businesses that primarily serve corporate, institutional and high net worth clients” (RBC).
There are 13 analysts from different financial firms that actively track and publish comments about the company’s stock (RBC investor relations). It shows that the company’s stocks are in high demand since the price is low. The analyst coverage for RBC is relatively sufficient according to the firm’s size, and it would benefit the investors by providing their professional opinions.
Risk management and factors impact the future profitability are covered in the previous criteria
Value criteria 7: Buy at attractive prices
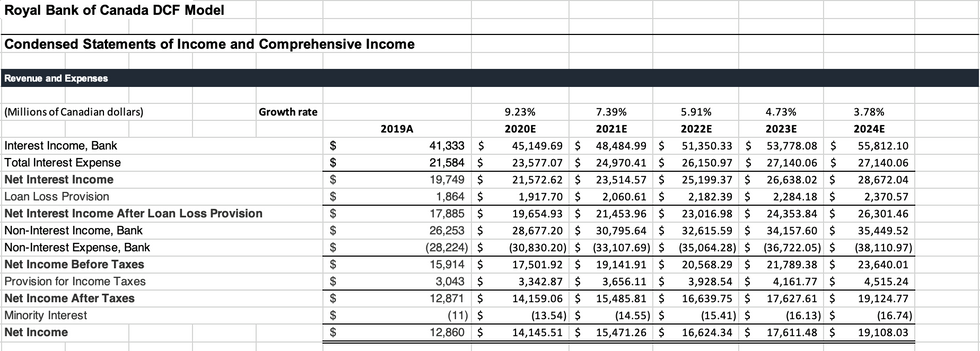
The DCF and DDM model are computed based on the information from the 2019 financial statements. The average of the two prices from two models give an expected fair price of $112.63, nearly a 13% premium to what RBC is currently worth ($99.62 as at Feb 28, 2020). RBC is currently a good value investment since we believe it to be underpriced by a good margin.
At a stock price of $112.63 RBC would have a P/E and P/B ratio of approximately 12.5 and 1.93 respectively.
Click to enlarge the model
* Some information is from previous value investment group project.